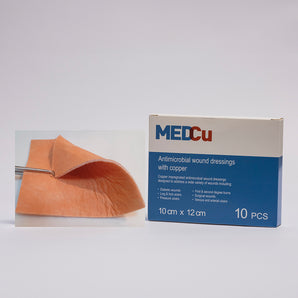
Key Takeaways
- Antimicrobial dressing are essential for preventing wound infections and promoting quicker healing by maintaining a moist environment and managing exudate.
- Different types of antimicrobial dressings, such as silver, iodine, honey, and PHMB-based options, cater to specific wound types and infection levels.
- Materials like foam, hydrocolloid, and gauze enhance dressing adaptability for various wound needs, ensuring effective infection control and comfort.
- Factors like wound type, exudate level, infection severity, and patient needs should guide the selection of the most suitable antimicrobial dressing.
- Advanced dressings with sustained antimicrobial activity, such as copper or silver-based options, offer superior protection but may involve higher costs or application complexity.
- Expert recommendations and clinical evidence underline the importance of tailoring dressing choices to individual wound conditions for optimal healing outcomes.
Choosing the right antimicrobial dressing for a wound is crucial for effective healing and infection prevention. With wounds being vulnerable to bacteria, fungi, and viruses, finding a solution that offers broad-spectrum protection while supporting the healing process is essential. Antimicrobial dressings not only minimise infection risks but also create an optimal environment for tissue repair.
Among the various options available, some dressings stand out due to their advanced design and innovative materials. These dressings, often incorporating elements like copper oxide, provide continuous antimicrobial activity and help manage exudate, ensuring the wound remains clean and conducive to healing. Understanding what makes a dressing effective can guide us in selecting the best option for wound care.
Understanding Antimicrobial Dressings
Antimicrobial dressings play a vital role in wound care by addressing infection risks and contributing to optimal healing conditions. These dressings integrate advanced technologies to manage both microbial activity and wound exudate effectively.
What Are Antimicrobial Dressings?
Antimicrobial dressings are specialised wound care solutions designed to prevent and control wound infections. They integrate antimicrobial agents, like silver, iodine, or copper, which inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. These dressings also maintain a moist environment, aiding tissue repair and promoting quicker recovery.
A variety of materials, including foam, hydrocolloid, and gauze, serve as the base for these dressings. For instance, copper-based antimicrobial wound dressings consist of multilayered, non-adherent materials incorporating copper oxide for persistent antimicrobial effects. By targeting a broad range of pathogens, they are effective in managing acute, chronic, or post-surgical wound complications.
How Do Antimicrobial Dressings Work?
Antimicrobial dressings follow dual strategies: antimicrobial activity and exudate management. Embedded antimicrobial agents neutralise pathogens directly at the wound site, disrupting the cellular structures of microbes to prevent their colonisation. Copper ions, for example, interact with bacterial membranes, causing oxidative stress and effectively halting their reproduction.
The exudate control mechanisms absorb and retain fluids essential for healing while minimising maceration risk. These dressings, such as those containing copper oxide, ensure continuous protection without hindering the natural healing processes. They also stimulate collagen production, enhancing tissue repair and ensuring wound recovery in a controlled environment.
Factors To Consider When Choosing A Dressing
Selecting the right antimicrobial dressings involves evaluating specific factors to ensure an optimal healing environment. Addressing these considerations supports both infection control and patient-specific wound care.
Type Of Wound
The wound type significantly determines the dressing choice. Acute wounds, like surgical incisions or burns, benefit from dressings that provide moisture balance and antimicrobial protection. Chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers or pressure sores, demand advanced antimicrobial wound dressings designed for long-term exudate management. Additionally, heavily exuding wounds require absorbent options like foam or hydrocolloid dressings.
Level Of Infection
Assessing infection severity is crucial when selecting antimicrobial dressings. For wounds with infection indicators (e.g., redness, swelling, or increased exudate), dressings containing antimicrobial agents like silver or iodine help eliminate pathogens. Deep or heavily contaminated wounds might require dressings with extended antimicrobial activity to prevent recurring infections. In contrast, uninfected wounds need preventive solutions that maintain a sterile environment.
Patient-Specific Needs
Patient needs dictate dressing specifications. Allergies to certain materials (e.g., latex) may necessitate hypoallergenic options. Mobility limitations or dressing change frequency often influence whether adhesive or non-adhesive dressings are appropriate. Age-related factors, like fragile skin in older adults, also affect dressing adherence and removal ease. Customised care ensures each patient receives the optimal wound management approach.
Top Types Of Antimicrobial Dressings
Selecting the right antimicrobial dressing is essential for promoting effective wound care and preventing infection. Various types of dressings are designed to address specific wound needs while offering antimicrobial properties and optimal healing environments.
Silver-Based Dressings
Silver-based antimicrobial dressings effectively combat a broad spectrum of bacteria. By disrupting bacterial cell walls, silver ions prevent infection and support wound healing. These dressings are suitable for moderate-to-high exudate wounds, such as pressure ulcers or those prone to infection. Their versatile formats, including foam and hydrogel, ensure adaptability for different wound sizes and locations.
Iodine-Based Dressings
Iodine-based dressings provide antimicrobial protection against bacteria and fungi. The iodine slowly releases into the wound, targeting pathogens while promoting healing. Ideal for chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers, these dressings also help manage slough and necrotic tissue. However, they're not recommended for individuals sensitive to iodine.
Honey-Based Dressings
Honey-based dressings utilise the natural antibacterial properties of medical-grade honey, reducing infection risks. These dressings maintain moisture balance, making them perfect for low-to-moderate exudate wounds like surgical incisions or minor burns. By fostering a favourable wound environment, honey-based options promote tissue repair and help remove harmful bacteria.
PHMB (Polyhexamethylene Biguanide) Dressings
PHMB dressings incorporate a polymer-based antimicrobial agent that inhibits bacterial growth at the wound site. They're effective for acute and chronic wounds, including surgical wounds and pressure injuries. Lightweight and non-adherent, these dressings reduce infection risks while ensuring easy application and removal.
Each type of dressing brings unique benefits and should be matched to the wound's characteristics to achieve optimal healing results.
Pros And Cons Of Popular Antimicrobial Dressings
Antimicrobial dressings are essential in wound care management, offering solutions to prevent infections and promote healing. Understanding their advantages and disadvantages helps determine the most appropriate choice based on individual wound needs.
Advantages
1. Broad-Spectrum Protection
Many dressings, particularly those using silver or copper, provide effective defence against bacteria, fungi, and viruses. For instance, copper-based antimicrobial wound dressings combat pathogens to reduce infection risks.
2. Enhanced Healing
Advanced dressings support tissue repair by creating an optimal healing environment. Formulations like honey-based dressings aid recovery by balancing moisture and encouraging collagen production.
3. Moisture Management
Dressings such as hydrocolloid retain a moist wound environment, which facilitates faster granulation and epithelialisation.
4. Reduced Dressing Changes
Some dressings, like foam-based or those with an extended wear time of up to seven days, minimise frequent changes, reducing patient discomfort and care costs.
5. Adaptability
Antimicrobial solutions are available in diverse materials, including gauze, foams, and hydrocolloids, offering options for varying levels of exudate and wound types.
Disadvantages
1. Allergic Reactions
Patients with sensitivities may react to agents like iodine or silver, though alternatives like PHMB dressings offer safer options.
2. Cost
Advanced options, such as silver-based and copper-integrated antimicrobial dressings, may have higher costs than traditional wound dressings.
3. Limited Use for Certain Wounds
Dressings intended for high-exudate wounds may not work effectively for dry or minimally exuding wounds. Honey-based dressings, for example, are better suited for low-to-moderate exudate wounds.
4. Application Complexity
Some dressings, particularly medical devices for chronic wound care, require professional application for optimal results, limiting accessibility in resource-constrained or rural areas.
Evaluating these factors allows healthcare providers to balance benefits against constraints, ensuring the selection of appropriate antimicrobial wound dressings for diverse patient needs.
Expert Opinions And Studies
Expert analyses and clinical evidence highlight the effectiveness of antimicrobial dressings in wound care. These insights guide healthcare providers in selecting products that prioritise patient recovery and infection control.
Clinical Evidence Supporting Antimicrobial Dressings
Research demonstrates the efficacy of antimicrobial dressings in reducing infection rates and accelerating wound healing. A study assessing copper-based antimicrobial dressings observed significant decreases in bacterial load, especially in chronic wound cases. Silver-based dressings, tested across acute and chronic wounds, showed broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and improved healing outcomes.
Moreover, evaluation of iodine-based dressings revealed effectiveness in managing biofilms, a challenge in infected and slow-healing wounds. These findings underscore that specific antimicrobial agents like copper or silver reduce the risk of complications while fostering a moist environment conducive to tissue regeneration.
A systematic review highlighted advanced dressings' dual role in wound exudate management and pathogen neutralisation. Foam-based antimicrobial dressings were particularly noted for handling heavy exudates, reducing the extent of maceration. Such evidence supports their inclusion in medical solutions designed to meet diverse wound care needs.
Recommendations From Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals emphasise tailoring antimicrobial dressing selection based on wound type, infection severity, and patient sensitivity. For instance, they frequently recommend Dynamed Pharmaceuticals' copper-integrated dressings for their prolonged antimicrobial activity against resistant pathogens. Silver-infused options are preferred for burns and moderate-to-high-exudate wounds, while iodine-based dressings remain a standard for chronic ulcers prone to fungal infections.
Experts also advise choosing medical devices that maintain balance by absorbing fluids while retaining enough moisture to promote granulation tissue development. They stress wound re-evaluation at dressing changes to identify shifts in healing needs. When advanced infections arise, they advocate combining antimicrobial dressings with proper systemic therapy for optimal results.
By integrating professional insights and evidence-based practices, antimicrobial dressings play a pivotal role in effective wound care across healthcare settings.
Conclusion
Choosing the best antimicrobial dressing requires careful consideration of the wound’s characteristics, the level of infection, and the patient’s unique needs. With options ranging from silver-based to honey-based dressings, each type offers distinct advantages that can significantly enhance healing and prevent complications.
By understanding how these dressings work and evaluating their benefits and limitations, we can make informed decisions that promote faster recovery and better outcomes. Tailoring the choice to the specific wound and regularly reassessing its progress ensures the most effective care for every patient.
Visit Dynamed Pharmaceuticals
Phone: 0861 00 00 43
Website: dynamed.co.za
Email (Sales): sales@dynamed.co.za
Email (Info): info@dynamed.co.za
Google Maps: Find us here
Frequently Asked Questions
What are antimicrobial dressings used for?
Antimicrobial dressings are specialised wound care solutions designed to prevent and manage infections. They incorporate agents like silver, iodine, or copper to neutralise pathogens, promote healing, and maintain a moist environment for tissue repair.
How do antimicrobial dressings improve wound healing?
Antimicrobial dressings work by killing or inhibiting harmful bacteria at the wound site, while also managing exudate. This dual action prevents infection, reduces inflammation, and creates an optimal environment for faster tissue regeneration.
What types of antimicrobial dressings are available?
Common types include silver-based, iodine-based, honey-based, and PHMB dressings. Each type offers specific benefits tailored to different wound characteristics, such as exudate levels, infection severity, and wound duration.
Are copper-based dressings beneficial for wound care?
Yes, copper-based dressings are effective in providing continuous antimicrobial activity, reducing bacterial loads, and managing exudate. Their persistent action makes them ideal for combating resistant pathogens.
Which wounds benefit most from antimicrobial dressings?
Antimicrobial dressings are suitable for acute or chronic wounds at risk of infection or those already infected. They are commonly used for burns, post-surgical wounds, ulcers, and other exudating injuries.
How do I choose the right antimicrobial dressing?
Selection depends on wound type, infection level, exudate amount, and patient-specific needs. For example, silver dressings are ideal for high-exudate wounds, while honey dressings suit low-exudate wounds.
Can antimicrobial dressings cause allergic reactions?
While uncommon, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to specific materials, like silver or iodine. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider before use, especially if there’s a known sensitivity.
Are antimicrobial wound dressings expensive?
Advanced antimicrobial dressings may be more expensive than standard options due to their specialised materials and features. However, their benefits in infection prevention and quicker healing often justify the cost.
How often should antimicrobial dressings be changed?
Change frequency depends on the wound and dressing type. Some require daily changes, while others can stay in place for several days, reducing discomfort and the risk of infection during dressing changes.
What is the clinical evidence supporting antimicrobial dressings?
Clinical studies show antimicrobial dressings reduce infection rates, lower bacterial loads, and promote faster healing. For example, silver and copper-based dressings have demonstrated broad-spectrum effectiveness against pathogens.
Are iodine-based dressings suitable for chronic wounds?
Yes, iodine-based dressings are effective for managing chronic wounds, especially those with biofilm infections. Their antibacterial and antifungal properties make them ideal for long-term wound care.
Do antimicrobial dressings help manage moisture?
Yes, antimicrobial dressings maintain a balanced moist environment, essential for healing. They absorb excess exudate to prevent maceration, keeping the wound site conducive to tissue repair.
Can antimicrobial dressings be used for uninfected wounds?
Yes, they can serve a preventive role by reducing the risk of infection in vulnerable wounds, such as post-surgical cuts or burns. However, evaluation by a healthcare professional is recommended.
Are antimicrobial dressings difficult to apply?
Most antimicrobial dressings are easy to use, but some advanced options may require specific techniques. Consult product guidelines or a healthcare provider for proper application instructions.
Why are silver-based dressings popular for wound care?
Silver-based dressings are highly effective against a broad range of bacteria, making them suitable for wounds with moderate to high exudate. Their proven antimicrobial properties ensure effective infection control.